Its very important to know about the SSL authentication concept in Loadrunner.
What Is SSL?
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a standard security technology for establishing an encrypted link between a server and a client—typically a web server (website) and a browser; or a mail server and a mail client (e.g., Outlook).
SSL allows sensitive information such as credit card numbers, social security numbers, and login credentials to be transmitted securely. Normally, data sent between browsers and web servers is sent in plain text—leaving you vulnerable to eavesdropping. If an attacker is able to intercept all data being sent between a browser and a web server they can see and use that information.
More specifically, SSL is a security protocol. Protocols describe how algorithms should be used; in this case, the SSL protocol determines variables of the encryption for both the link and the data being transmitted.
SSL secures millions of peoples’ data on the Internet every day, especially during online transactions or when transmitting confidential information. Internet users have come to associate their online security with the lock icon that comes with an SSL-secured website or green address bar that comes with an extended validation SSL-secured website. SSL-secured websites also begin with https rather than http.
How Does the SSL Certificate Create a Secure Connection?
When a browser attempts to access a website that is secured by SSL, the browser and the web server establish an SSL connection using a process called an “SSL Handshake” (see diagram below). Note that the SSL Handshake is invisible to the user and happens instantaneously.
Essentially, three keys are used to set up the SSL connection: the public, private, and session keys. Anything encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key, and vice versa.
Because encrypting and decrypting with private and public key takes a lot of processing power, they are only used during the SSL Handshake to create a symmetric session key. After the secure connection is made, the session key is used to encrypt all transmitted data.
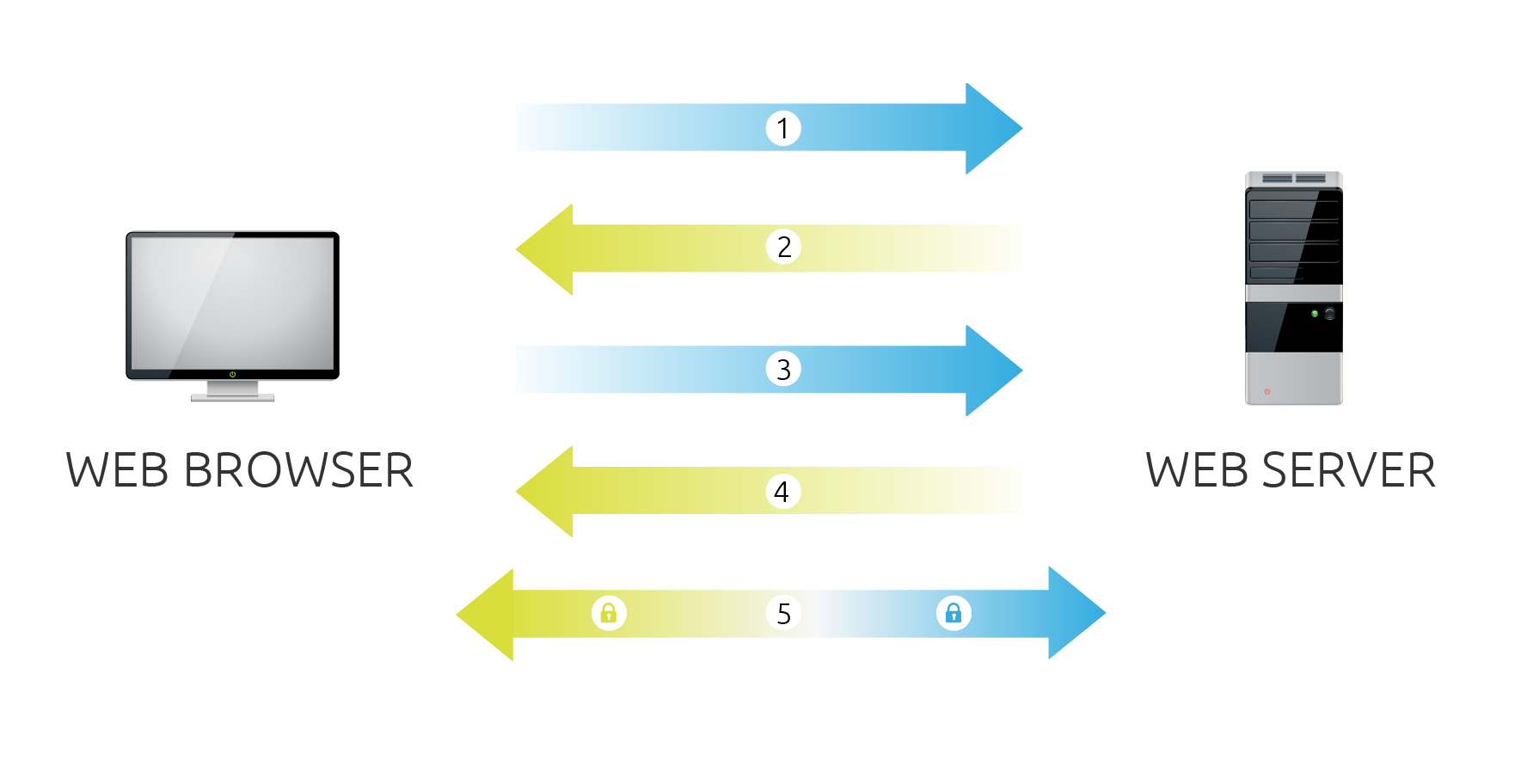
- Browser connects to a web server (website) secured with SSL (https). Browser requests that the server identify itself.
- Server sends a copy of its SSL Certificate, including the server’s public key.
- Browser checks the certificate root against a list of trusted CAs and that the certificate is unexpired, unrevoked, and that its common name is valid for the website that it is connecting to. If the browser trusts the certificate, it creates, encrypts, and sends back a symmetric session key using the server’s public key.
- Server decrypts the symmetric session key using its private key and sends back an acknowledgement encrypted with the session key to start the encrypted session.
- Server and Browser now encrypt all transmitted data with the session key.
How do I identify the SSL protocols and certificates used by a website when testing with LoadRunner
Cause -Understanding the SSL Protocols and certificates used by a website.
Solution -To identify the type of SSL and certs used on a web server, type the following commands from a Loadrunner client workstation :
Go to the Loadrunner/bin directory.
Type "openssl", this will then display an >openssl prompt.
Type OpenSSL>s_client - connect test.com:443 where test.com is your web site.
Note: if you are not sure about the port open the developer tool in chrome and hit the URL. It will display IP address, port etc.
This will then return details of the web servers SSL connections with different ciphers, TLS versions, and SSL server certificate analysis.
Other useful commands to use in LoadRunner Web protocol scripts are as follows:
web_set_sockets_option("SHUTDOWN_MODE", "FAST");Allows the disconnection of the SSL session to be completed quickly.
web_set_sockets_option("SSL_VERSION", "TLS");
web_set_sockets_option("SSL_CIPHER_LIST", "RC4-MD5");These options allow the version and cipher for SSL to be specified. Possible versions and ciphers are detailed in the Loadrunner Function Reference.
web_set_sockets_option("TRACE_SSL_IO","1");This option will detail all SSL IO in the normal vuser log.
web_set_sockets_option("PRINT_SSL_INFO","1");This option will detail the version and certificate used in the SSL configuration.
web_set_sockets_option("PROXY_INITIAL_BASIC_AUTH","0");This option disables the initial Basic authentication.
Connections per second:
Number of TCP/IP connections opened
Number of Connections Shutdown. No of connections is fraction of hits/sec
TCP/IP connections are expensive interms of server, router and network resource consumption. So HTTP request should use same connection instead of opening new connection each time of each request.
SSL connections per second:
No of SSL connections opened per second
After TCP/IP connection SSL connection is opened.
SSL connection has heavy resource consumption.
If we select simulate new user at each iteration then there should not be more than one SSL connection per sec









